MALE PATTERN HAIR LOSS
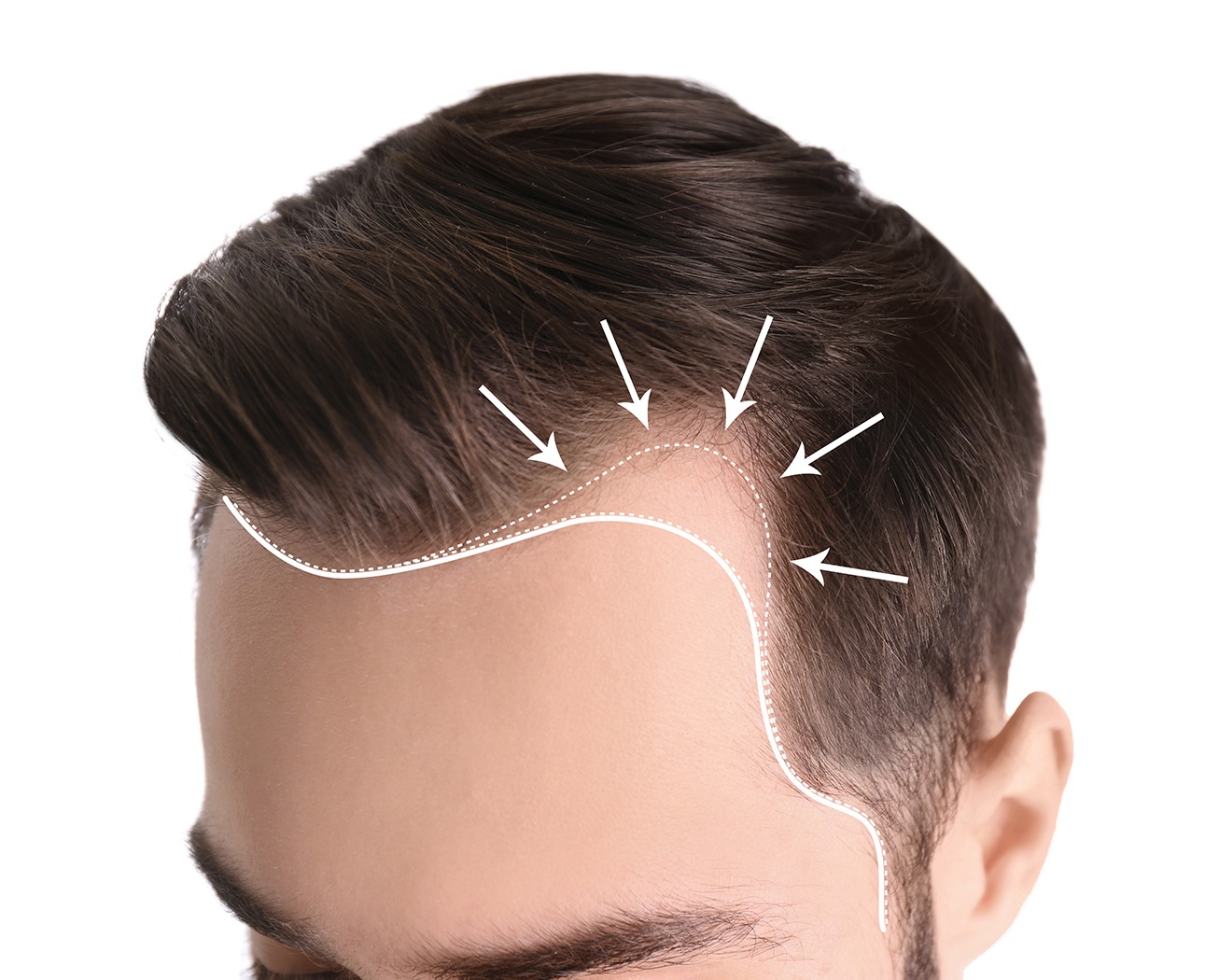
Male Pattern Hair Loss is the most common type of hair loss in men. In Male Pattern Hair Loss, the hair on the top of your head and temples begins to thin. Over time, the hair on the temples regresses even more, leaving only hair in the middle of the front of the head, and an increasingly bald area appears on the top.
Then, the areas where hair is lost on the front and top of the head come together, and the top of the head becomes completely bald. Eventually, all that remains is the hair on the sides and back of the head.
Male Pattern Hair Loss is an unwanted and stressful experience for many men.
This condition occurs in some men in their early twenties.
Male Pattern Hair Loss (androgenetic alopecia) is the most common type of hair loss in men, affecting 25% of men up to the age of 25, 40% up to the age of 40, and 50% up to the age of 50.
Why? Guilty Genes!
Male Pattern Hair Loss is usually hereditary and is a real concern for many men.
Men inherit this trait from their mother's and father's family tree. If you are genetically programmed to lose your hair and can't do anything about your hair loss, your chances of keeping it in the long term are very low.
Male Pattern Hair Loss is a condition outside of the normal hair cycle. Androgenetic alopecia, as its name suggests, is due to a genetic cause.
DHT: "Bad" Testosterone
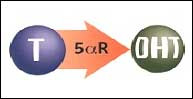
DHT is one of the many male hormones in the body. DHT is important in the early developmental stages of a man’s life; however, it becomes the cause of hair loss as men age. DHT shrinks the hair follicle so that it cannot produce visible hair.
DHT plays a major role in male pattern baldness.
Formation of DHT
Effect of DHT on hair follicle
Male Pattern Hair Loss is caused by the activity of DHT (dihydrotestosterone) on hair follicles.
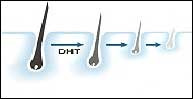
Human hair normally follows a cycle that includes growth, shedding, and regrowth. However, increased levels of DHT are thought to contribute to a shorter growth phase and a shorter time required for hair to fall out, leading to thinning hair.
Conditions where DHT contributes;
- Shortening of the growth phase of HAIR
- Progressive miniaturization of HAIR follicles
- Reduction in terminal hair count
*DHT: Dihydrotestosterone